The Complete Beginner’s Guide to Starting Your Amazon Business
The Amazon marketplace has transformed from an online bookstore into a global e-commerce powerhouse, creating unprecedented opportunities for entrepreneurs at every level. With over 300 million active customers and 2.5 million active sellers worldwide, Amazon offers a robust platform where even complete beginners can build profitable businesses without extensive experience or technical knowledge.
Whether you’re looking to create a side hustle or establish a full-time enterprise, starting an Amazon business provides flexible entry points with relatively low barriers to entry. The beauty of selling on Amazon lies in its established infrastructure – from built-in traffic to warehousing solutions – that allows new sellers to focus on product selection and growth rather than building systems from scratch.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll discover everything you need to know to launch your Amazon business, including step-by-step instructions for setting up your seller account, researching profitable products, sourcing inventory, optimizing listings, handling fulfillment, and marketing your products to generate sales. We’ll break down complex concepts like FBA (Fulfillment by Amazon) and FBM (Fulfillment by Merchant) into practical steps you can implement immediately, regardless of your experience level.
Understanding the Amazon business model
Before diving into the tactical aspects of selling on Amazon, it’s essential to understand the different business models available to you as a seller. Each approach has distinct advantages, investment requirements, and growth potential.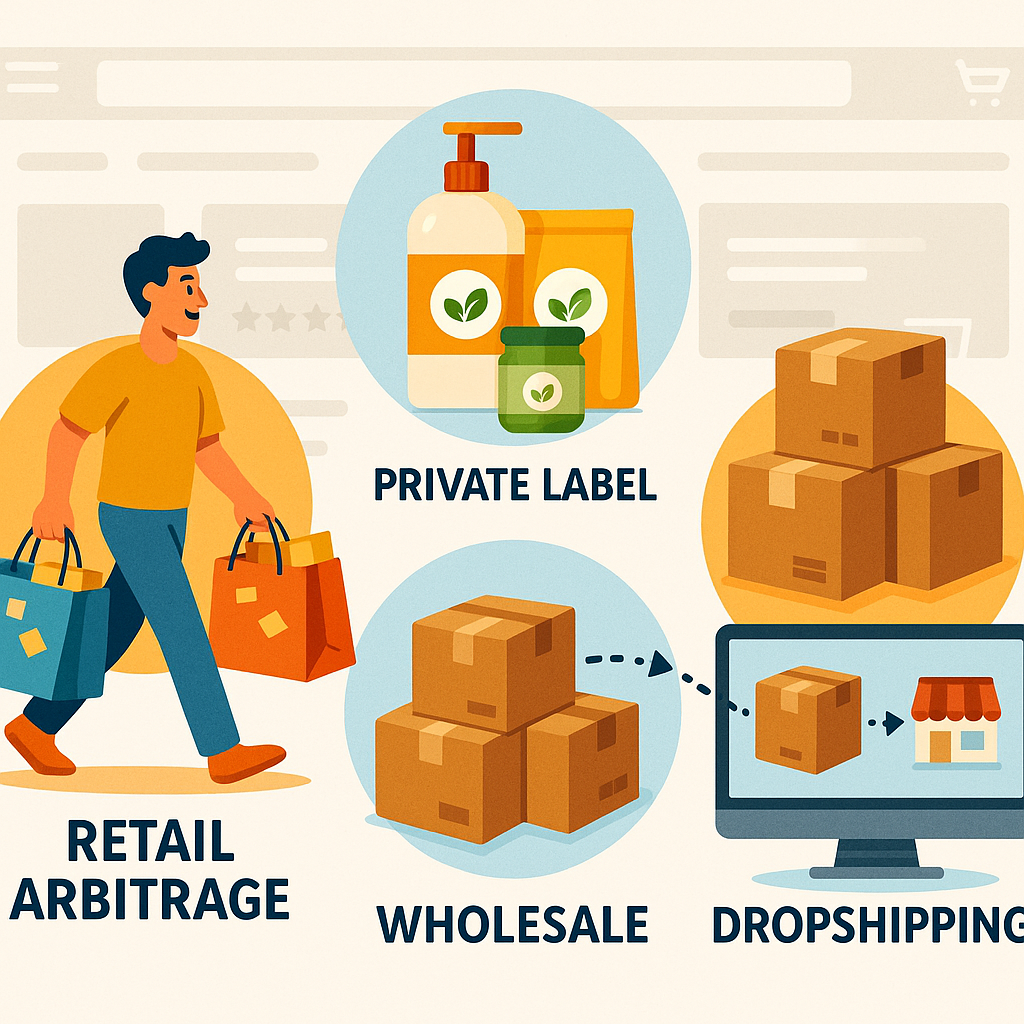
Pros and cons of each Amazon selling model
Retail Arbitrage: This model involves purchasing discounted products from retail stores and reselling them on Amazon at a higher price. With a low barrier to entry (you can start with as little as $100-$500), retail arbitrage allows you to test the waters before making significant investments. However, this model can be time-consuming, challenging to scale, and comes with sustainability concerns as finding consistent deals requires ongoing effort.
Private Label: This approach involves sourcing generic products from manufacturers and selling them under your own brand. While requiring a higher initial investment ($1,000-$5,000+), private label offers better profit margins, brand control, and greater long-term growth potential. The learning curve is steeper, but the ability to build a recognizable brand provides significant advantages.
Wholesale: Purchasing products in bulk directly from established brands and reselling them on Amazon characterizes the wholesale model. This method requires moderate startup capital ($2,000-$10,000) and offers reliable inventory sources but comes with lower profit margins and increased competition from other sellers offering identical products.
Dropshipping: With this hands-off approach, you list products for sale without holding inventory; when orders come in, the supplier ships directly to the customer. While requiring minimal capital to start, dropshipping on Amazon faces strict policy restrictions and potential fulfillment challenges that can affect your account health.
Amazon FBA vs. FBM: These fulfillment options determine how your products reach customers:
- Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA): Amazon stores your inventory, picks, packs, and ships orders, handles customer service, and processes returns. This option saves time, enables Prime eligibility, and simplifies scaling but incurs storage and fulfillment fees that impact profit margins.
- Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM): You manage all aspects of inventory storage, shipping, and customer service. This approach provides complete control and potentially higher margins but requires significant time investment and operational infrastructure as your business grows.
Many successful Amazon sellers combine these models or transition between them as their business evolves. For beginners, starting with retail arbitrage or a small private label product using FBA often provides the best balance of accessibility and growth potential.
Setting up your Amazon seller account
Establishing your presence on Amazon begins with creating a seller account that serves as your business hub. The setup process requires attention to detail to ensure approval and prevent future complications.
Navigating Amazon Seller Central
Step 1: Choose your account type
Amazon offers two seller account options:
- Individual account: No monthly subscription fee but charges $0.99 per item sold plus referral fees. Ideal if you plan to sell fewer than 40 items monthly.
- Professional account: $39.99 monthly subscription with no per-item fee. Provides access to advanced selling tools, bulk listing capabilities, and eligibility for top placement on product pages.
Step 2: Gather required information
Before beginning registration, prepare:
- Business email address or Amazon customer account
- Credit card that can be charged internationally
- Government-issued ID (passport or driver’s license)
- Tax information (SSN for individuals or EIN for businesses)
- Phone number for verification
- Bank account information for deposits
Step 3: Complete the registration process
- Visit sell.amazon.com and click “Sign up”
- Choose between Individual and Professional selling plans
- Log in with your existing Amazon account or create a new one
- Verify your identity with the required documents
- Set up your seller profile with business information
- Set up your billing method and deposit information
- Complete tax interview questions
Step 4: Navigate Seller Central
Once approved, familiarize yourself with key Seller Central areas:
- Dashboard: Overview of account health, sales, and performance metrics
- Inventory: Manage product listings, stock levels, and FBA shipments
- Orders: View and process customer purchases
- Advertising: Create and manage Amazon PPC campaigns
- Reports: Access detailed sales data and business analytics
- Performance: Monitor account metrics and customer feedback
- Help: Access seller support and resource library
For optimal account health, regularly monitor your performance metrics, especially Order Defect Rate, Late Shipment Rate, and Pre-fulfillment Cancel Rate, as these directly impact your selling privileges. Setting up two-factor authentication adds an essential layer of security to protect your business from unauthorized access.
Conducting product research and finding winning products
Selecting the right products represents perhaps the most crucial decision in your Amazon business journey. Thorough research helps identify opportunities with strong demand, manageable competition, and healthy profit potential.
Validating product ideas
Key product selection criteria:
- Demand: Look for products with consistent search volume and sales of at least 300 units per month across the top 10 listings
- Competition: Seek niches where existing sellers have fewer than 500 reviews or suboptimal listings you can improve upon
- Price point: Products priced between $15-$50 typically balance affordability for customers with sufficient margin for profitability
- Size and weight: Smaller, lighter items reduce shipping and storage fees
- Seasonality: Products with year-round demand provide more stable revenue
- Differentiation potential: Opportunities to improve upon existing products through quality, features, or branding
- Simplicity: Products with fewer components have lower defect rates
Research methods for beginners:
1. Manual research: Start by browsing Amazon’s Best Sellers, New Releases, and Movers & Shakers lists. Look for patterns in successful products and read customer reviews to identify common complaints that your product could address. The “Customers also bought” section provides insights into complementary product opportunities.
2. Keyword research: Use Amazon’s search bar to identify popular products. As you type, Amazon’s autocomplete suggestions reveal common search terms. Tools like Google Trends help evaluate long-term interest in product categories.
3. Competition analysis: Examine competing listings for:
- Number and quality of reviews
- Listing quality (images, descriptions, bullet points)
- Best Seller Rank (lower numbers indicate higher sales)
- Number of sellers offering the same product
4. Dedicated research tools: While beginners can start with manual research, specialized tools provide data-driven insights:
- Jungle Scout: Offers sales estimators, product trackers, and opportunity finders
- Helium 10: Provides keyword research, competitor analysis, and profitability calculators
- AMZScout: Features product database, keyword tools, and FBA fee calculators
Avoiding restricted products: Amazon prohibits or restricts numerous categories that new sellers should avoid, including:
- Most electronics and accessories
- Certain beauty products
- Food and grocery items
- Products with safety concerns
- Items with intellectual property restrictions
Check Amazon’s restricted products guidelines before investing in inventory.
Remember that successful product research balances quantitative data with qualitative insights. The goal is finding products with proven demand but opportunities for improvement that align with your budget and business goals.
Sourcing products and managing inventory
After identifying promising product opportunities, the next step involves finding reliable suppliers and establishing inventory management systems. Your sourcing strategy significantly impacts product quality, cost structure, and operational efficiency.
Sourcing options for new Amazon sellers:
1. Overseas manufacturers: Platforms like Alibaba connect sellers with thousands of manufacturers, primarily in Asia. While offering the lowest unit costs, international sourcing involves longer lead times (30-60 days), higher minimum order quantities (MOQs), and more complex logistics. Communication challenges and quality control concerns require careful supplier vetting.
2. Domestic wholesalers: Working with suppliers in your home country typically provides faster shipping, easier communication, and lower MOQs. Though unit costs run higher than overseas options, reduced shipping expenses and faster inventory turns may offset this disadvantage. Search platforms like ThomasNet (US), Faire, or industry-specific trade shows to find legitimate wholesalers.
3. Print-on-demand services: For customized products like t-shirts, mugs, or posters, print-on-demand services manufacture items only when ordered. This approach eliminates inventory risk but typically yields lower profit margins and less control over product quality.
4. Local sourcing: Retail arbitrage sellers source products from clearance sections, liquidation sales, and discount stores. While requiring more time investment, local sourcing allows hands-on product inspection and immediate inventory availability.
Evaluating potential suppliers:
- Communication responsiveness: Professional responses within 24-48 hours indicate reliability
- Sample quality: Always order samples before committing to larger purchases
- Minimum order requirements: Negotiate lower MOQs for initial orders when possible
- Production capacity: Ensure suppliers can scale with your business growth
- Payment terms: Seek favorable terms like 30% deposit/70% upon completion
- References/verification: Request client references and verify business credentials
Warning signs of problematic suppliers:
- Unwillingness to provide samples
- Requests for payment via unsecured methods (Western Union, cryptocurrency)
- Reluctance to sign agreements or provide quality guarantees
- Significant discrepancies between sample quality and bulk orders
- Poor communication or unexplained delays
Inventory management fundamentals:
Effective inventory control prevents both stockouts (lost sales) and excess inventory (increased storage fees). Calculate your optimal inventory levels by considering:
- Lead time: Time from placing an order to receiving inventory
- Sales velocity: Units sold per day/week
- Seasonal fluctuations: Demand variations throughout the year
- Storage costs: Amazon’s tiered storage fees increase for inventory stored beyond 365 days
For FBA sellers, create a reordering system triggered when inventory reaches approximately twice your lead time in remaining stock. This buffer protects against unexpected sales spikes or supplier delays while minimizing long-term storage fees.
Creating and optimizing your Amazon listings
Your product listing serves as the virtual salesperson for your Amazon business. Well-crafted listings not only improve visibility in Amazon’s search algorithm but also convert browsers into buyers by addressing customer questions and concerns.
Amazon listing mistakes to avoid
Elements of an optimized Amazon listing:
1. Product title (200 character limit): Front-load your title with the most important keywords while maintaining readability. Include:
- Brand name
- Product name
- Key features (material, size, color, quantity)
- Distinguishing characteristics
Example: “BrandName Bamboo Cutting Board Set – Large & Medium Organic Wood Chopping Boards with Juice Groove – Kitchen Prep Surfaces for Meat & Vegetables”
2. Bullet points (5-7 recommended): Highlight the most compelling benefits and features in scannable format. Structure each bullet to address specific customer needs, beginning with the benefit followed by supporting features. Focus on answering: “Why should customers choose your product over competitors?”
3. Product description: Expand on information from bullets while incorporating additional keywords naturally. Use short paragraphs, subheadings, and narrative elements to create an engaging, informative description that builds confidence in the purchase decision.
4. Backend keywords: In Seller Central, add relevant search terms not included in your visible listing. Avoid repeating words already used in your title or bullets, and don’t include competitors’ brand names (which violates Amazon’s policies).
5. Images: High-quality images significantly impact conversion rates. Include:
- Main image: Clean, professional product photo on white background
- Lifestyle images showing the product in use
- Size reference images with familiar objects
- Infographics highlighting key features
- Packaging photos
- Close-ups of important details
All images should be at least 1000×1000 pixels to enable zoom functionality.
6. A+ Content: Professional sellers with brand registry access can create enhanced product descriptions with formatted text, comparison charts, and additional images. This premium content improves conversion rates by 3-10% on average.
7. Pricing strategy: Research competitor pricing while accounting for all costs:
- Product cost
- Shipping to Amazon
- Amazon fees (referral, FBA, etc.)
- Return rate allowance
- Marketing costs
- Desired profit margin
Consider offering introductory pricing to generate initial reviews before adjusting to your target price point.
Common optimization mistakes:
- Keyword stuffing that makes titles unreadable
- Generic product descriptions that fail to differentiate from competitors
- Poor image quality or insufficient image variety
- Neglecting to address common customer questions or concerns
- Ignoring negative reviews instead of using them to improve listings
- Failing to update listings as the marketplace evolves
Regularly analyze your listing’s performance through Seller Central reports, making data-driven improvements to enhance visibility and conversion rates. Monitor which search terms drive traffic to your listings and incorporate high-performing terms more prominently in your content.
Fulfilling, shipping, and handling customer service
Efficient fulfillment operations ensure customers receive their purchases promptly and in excellent condition. Your choice between FBA and FBM significantly impacts operational complexity, customer experience, and overall profitability.
Amazon FBA process overview:
- Inventory preparation: Products must meet Amazon’s packaging and labeling requirements:
- Each product needs a scannable barcode (manufacturer UPC/EAN or Amazon FNSKU)
- Fragile items require additional packaging protection
- Products with special requirements (e.g., lithium batteries, liquids) need hazmat approval
- Expiration dates must be clearly visible for applicable products
- Creating shipment plans: In Seller Central, specify:
- Products and quantities being sent
- Whether products are individually labeled or require Amazon labeling (for an additional fee)
- Shipping method (partnered carrier or your own)
Amazon then assigns inventory to specific fulfillment centers.
- Shipping to Amazon: Package inventory according to Amazon’s guidelines:
- Box weight limitations (typically under 50 lbs)
- Proper labeling of each box with shipping labels
- Content information on the outside of each box
- Inventory processing: Once received, Amazon typically makes inventory available for sale within 1-3 days.
FBA fees include:
- Fulfillment fees (based on size/weight)
- Monthly storage fees (per cubic foot)
- Long-term storage fees (for inventory older than 365 days)
- Optional services (removal, disposal, returns processing)
Amazon FBM requirements:
If handling fulfillment yourself, establish efficient systems for:
- Order management: Processes for receiving, processing, and tracking orders
- Packaging materials: Professional packaging that protects products during transit
- Shipping options: Reliable carriers with tracking capabilities
- Meeting SLA requirements: Adhering to Amazon’s service level agreements for shipping timeframes (typically 1-2 business days)
Customer service excellence:
Regardless of fulfillment method, delivering exceptional customer service drives positive reviews, repeat purchases, and account health:
- Response time: Answer customer inquiries within 24 hours
- Proactive communication: Notify customers of any potential delays or issues
- Returns handling: Process returns promptly and issue refunds within Amazon’s required timeframes
- Review management: Respond professionally to both positive and negative reviews
For FBA sellers, Amazon handles most customer service aspects, but you should monitor performance metrics and address any underlying product issues that generate returns or negative feedback. FBM sellers bear greater responsibility for the entire customer experience and must maintain systems that ensure consistent satisfaction.
Marketing, reviews, and growing your Amazon business
Once your products are listed and available, implementing strategic marketing initiatives drives visibility and sales momentum. A comprehensive marketing approach combines Amazon’s internal tools with external channels to maximize exposure.
Leveraging Amazon advertising and promotions
Amazon PPC advertising:
Pay-per-click advertising represents the fastest way to gain visibility for new listings. Amazon offers several campaign types:
- Sponsored Products: Product-level ads appearing in search results and product detail pages
- Start with automatic campaigns to discover converting keywords
- Set daily budget limits ($10-$20 for beginners)
- Begin with conservative bids ($.50-$1.00)
- After 1-2 weeks, analyze search term reports
- Create manual campaigns targeting high-converting keywords
- Add negative keywords to eliminate unprofitable terms
- Sponsored Brands: Banner ads featuring your logo and multiple products
- Sponsored Display: Retargeting ads reaching shoppers who viewed your products
Launch promotions:
- Lightning Deals: Limited-time offers featured in Amazon’s Deal sections
- Coupons: Clickable savings displayed in search results
- Percentage discounts: Promotions shown on product pages
- Buy One Get One: Effective for encouraging larger order values
Building customer reviews:
Reviews significantly impact conversion rates and organic ranking. Ethical methods for generating reviews include:
- Amazon’s “Request a Review” button: Available 4-30 days after purchase
- Automated review requests: Tools that send review requests at optimal times
- Product inserts: Thank you cards with QR codes linking to your Amazon storefront (avoid directly requesting reviews)
- Exceptional product quality: The most sustainable review generation method
- Amazon Vine program: Available to brand-registered sellers with fewer than 30 reviews
External traffic strategies:
- Social media marketing: Building audiences on platforms aligned with your product demographics
- Email marketing: Developing an email list through product inserts or external websites
- Content marketing: Creating valuable content addressing problems your products solve
- Influencer partnerships: Collaborating with relevant content creators
Scaling and expansion:
As your business gains traction, consider these growth avenues:
- Product line expansion: Adding complementary products to increase average order value
- International marketplaces: Expanding to Amazon’s global marketplaces
- Multi-channel selling: Adding your own website or other platforms
- Brand Registry: Unlocking advanced tools and protection
- Amazon Programs: Applying for programs like Subscribe & Save or Amazon Business
Track key performance metrics regularly, including Advertising Cost of Sale (ACoS), conversion rate, organic ranking for target keywords, and customer lifetime value. Use these insights to refine your strategy and allocate resources to the most profitable activities.
Remember that Amazon’s algorithm rewards products with strong sales history, making the early launch phase critical. Invest appropriately in PPC and promotions during this period to establish momentum that drives long-term organic success.
Conclusion
Building a successful Amazon business requires patience, continuous learning, and strategic execution across multiple disciplines. By following this roadmap, you’ve gained a comprehensive understanding of the essential steps – from selecting a business model and creating your seller account to finding winning products, optimizing listings, managing fulfillment, and marketing effectively.
The most successful Amazon entrepreneurs approach the platform as a legitimate business rather than a get-rich-quick scheme. They focus on solving customer problems through quality products, efficient operations, and exceptional service. While challenges will inevitably arise, the systematic approach outlined in this guide provides the foundation needed to navigate obstacles and build a sustainable, profitable business.
Start by taking focused action on one section at a time. Begin with seller account creation, then move methodically through product research, sourcing, listing creation, and marketing. Document your processes and learn from both successes and setbacks. Connect with other Amazon sellers through forums, Facebook groups, or local meetups to share knowledge and stay current with platform changes.
With consistent effort and strategic adaptation, your Amazon business can evolve from a beginner venture into a significant income stream or even a full-time enterprise. The journey starts with a single step – take that step today and join the millions of entrepreneurs who have found success in the world’s largest online marketplace.
Frequently asked questions
How much money do you need to start an Amazon business?
Most beginners can start with $500–$2,500, but costs vary by business model, product choice, and initial order size.
Do I need a business license to sell on Amazon?
Typically, Amazon only requires identity verification and tax info for starter accounts, but local laws may require business registration.
How long does it take to become profitable on Amazon?
It often takes 3–6 months to see profit, depending on niche, investment, and marketing efforts.
Is it better to use Amazon FBA or FBM as a beginner?
FBA is easier for new sellers who want Amazon to handle shipping and returns, though FBM may suit small or unique products.
Can you start an Amazon business without inventory?
Yes, via dropshipping or print-on-demand, but most successful businesses opt to manage their own stock for quality control and profitability.
